
This splint will be used preoperatively to immobilize the fracture as a customized stabilizing tool during the operation and then will serve as a resting splint postoperatively ( Figs. The patients that fit the above characteristics when seen in the clinic are reviewed by the specialist hand therapist who measures and fabricates a modification of the POSI splint. We developed a novel care pathway for patients deemed appropriate for MC ORIF fracture stabilization. In our institution, all the patients with MC fractures that undergo ORIF will be followed up by our hand therapy colleagues and a thermoplastic splint will be custom fabricated based on the anatomy of the patient with variants upon the position of safe immobilization (POSI). Customized patient-precise instruments for hand surgery have been described before and are developed using additive manufacturing technology such as 3-dimensional printing, but there is no description of a device that inhibits the hand from supinating. These solutions are frequently inadequate as the hand is repositioned multiple times throughout the procedure due to the natural tendency of the arm to supinate. Some surgeons resort to a sterile crepe bandage or a “kidney” dish as a makeshift stand to help the assistant hold the hand in a fixed position. Every time C-arm radiography is used the assistant must reposition the hand which is both time consuming and impairs the fluency of the procedure.

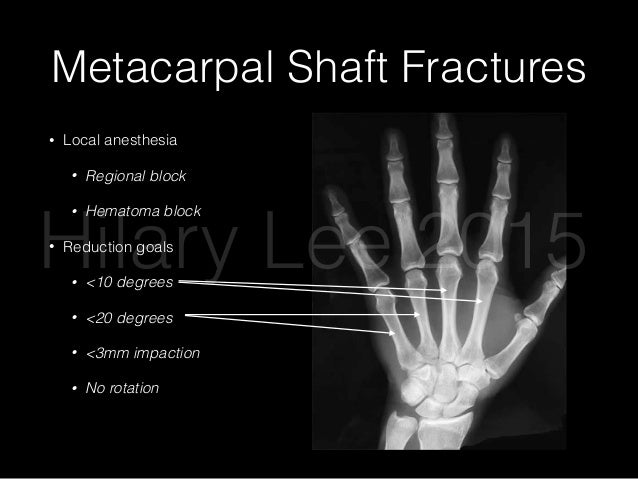
C-arm radiography is required during this procedure for visualization of fracture site and confirmation of metal work placement. Ĭurrently, the ORIF technique for MC fracture fixation is performed with the use of an assistant who holds the hand in a static pronated position for the operating surgeon, allowing ease of access to the fracture site. Multiple studies have shown that open reduction and internal fixation (ORIF) allows for early mobilization compared to intramedullary pinning fixation and is a frequent procedure performed for MC fractures. The alignment of the broken metacarpal directly and hold the pieces in place with tiny metal plate and screws.Fractures of the metacarpal (MC) bones account for a significant part of fractures in the hand up to 40% as described in the literature with a shaft versus neck ratio of roughly 1:2.
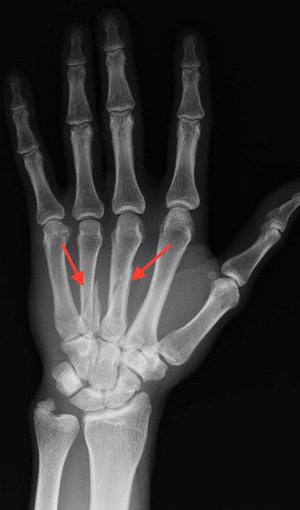
If the fracture is severe, it may be necessary to make a small incision over the back of the hand to restore
#3rd metacarpal fracture splint skin
If the metacarpal can be set straight, metal wires are placed through the skin and into the bone to keep it straight while it is healing. A regional block numbing of the arm is performed, and Operative Treatment: Surgical repair of metacarpal fractures is required when the fracture pieces are unstable (won’t stay in place), or not healing properly with cast treatment. Occasionally the fracture needs to be numbed up and “set” straight. Nonoperative Treatment: Splinting and casting are the mainstays of nonoperative treatment of metacarpal fractures that are stable and not badlyĭisplaced (out of alignment). Undesirable outcomes such as nonunion (won’t heal) or malunion (heals crooked). Even without these warning signs, it is best to seek urgent treatment as the results of delayed treatment of metacarpal fractures can lead to Significant deformity of the hand or any open wounds around the hand (possible open or compound fracture). Suspected hand fractures warrant emergent treatment if you are experiencing hand numbness and tingling, severe or “tight” swelling, X-rays usually offer definitive diagnosis and help with treatment planning. Yes! Often fractures are obvious on physical examination, but severe sprains and contusions can also look and feel very much like a metacarpal fracture. Is There a Test for Metacarpal Fractures?


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
